Notebooks
Premium
Trends

BioTuring
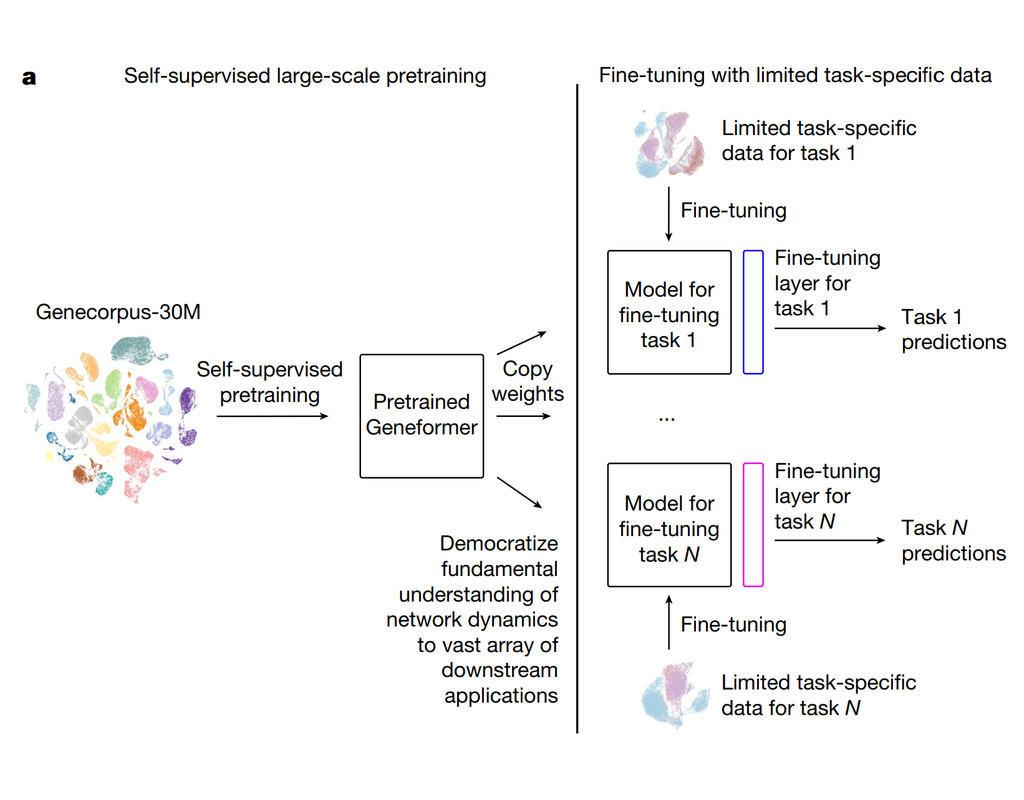
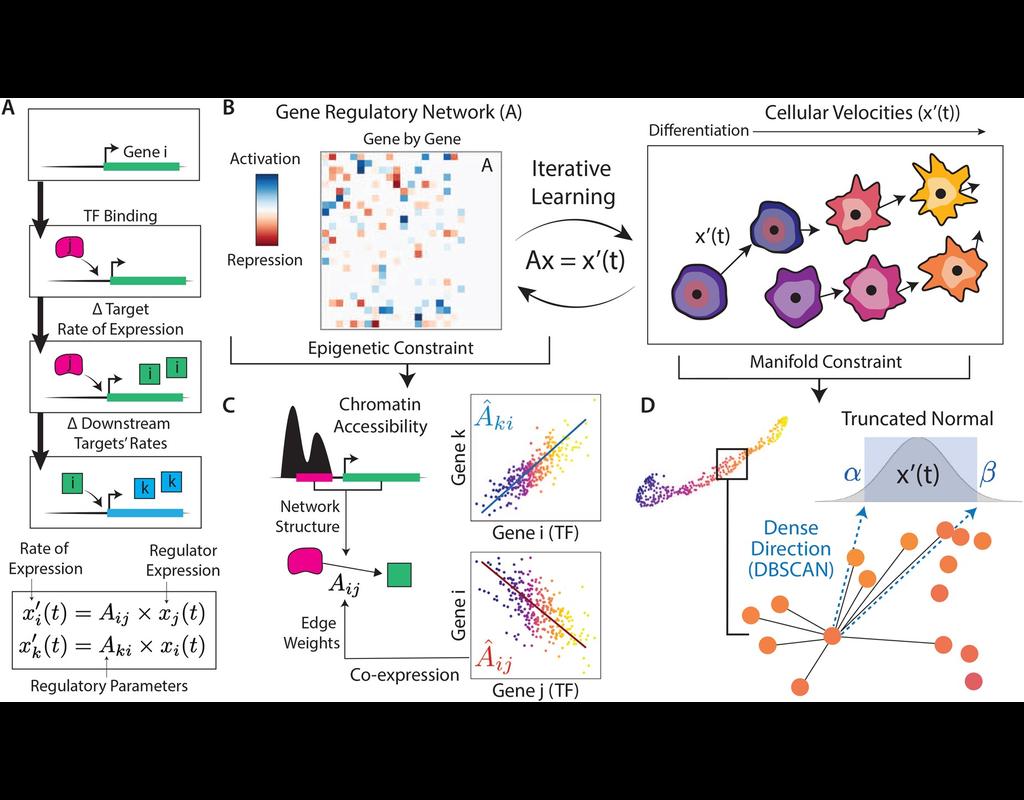
scPRINT is a large transformer model built for the inference of gene networks (connections between genes explaining the cell's expression profile) from scRNAseq data.
It uses novel encoding and decoding of the cell expression profile and new pre-training methodologies to learn a cell model.
scPRINT can be used to perform the following analyses:
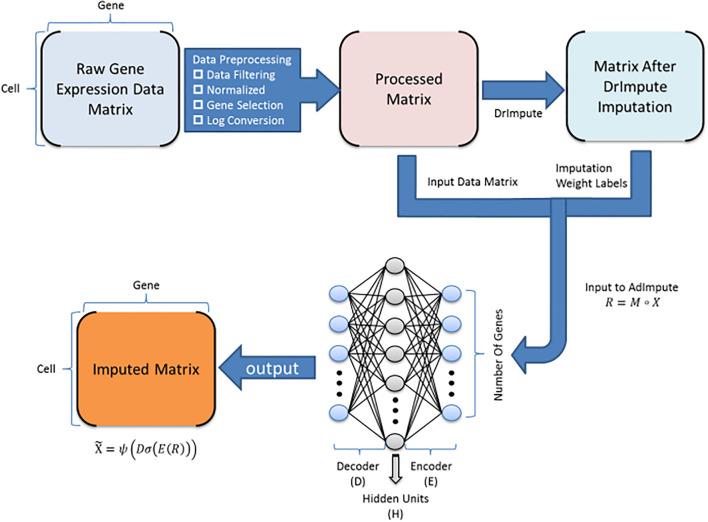
- expression denoising: increase the resolution of your scRNAseq data
- cell embedding: generate a low-dimensional representation of your dataset
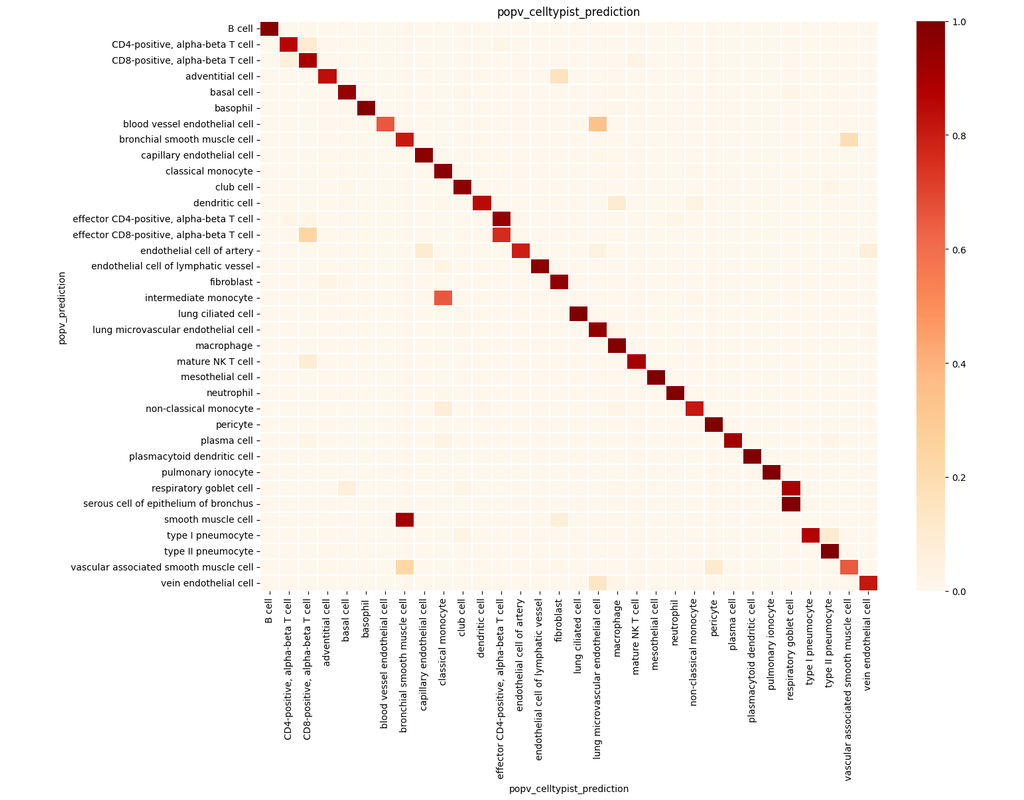
- label prediction: predict the cell type, disease, sequencer, sex, and ethnicity of your cells
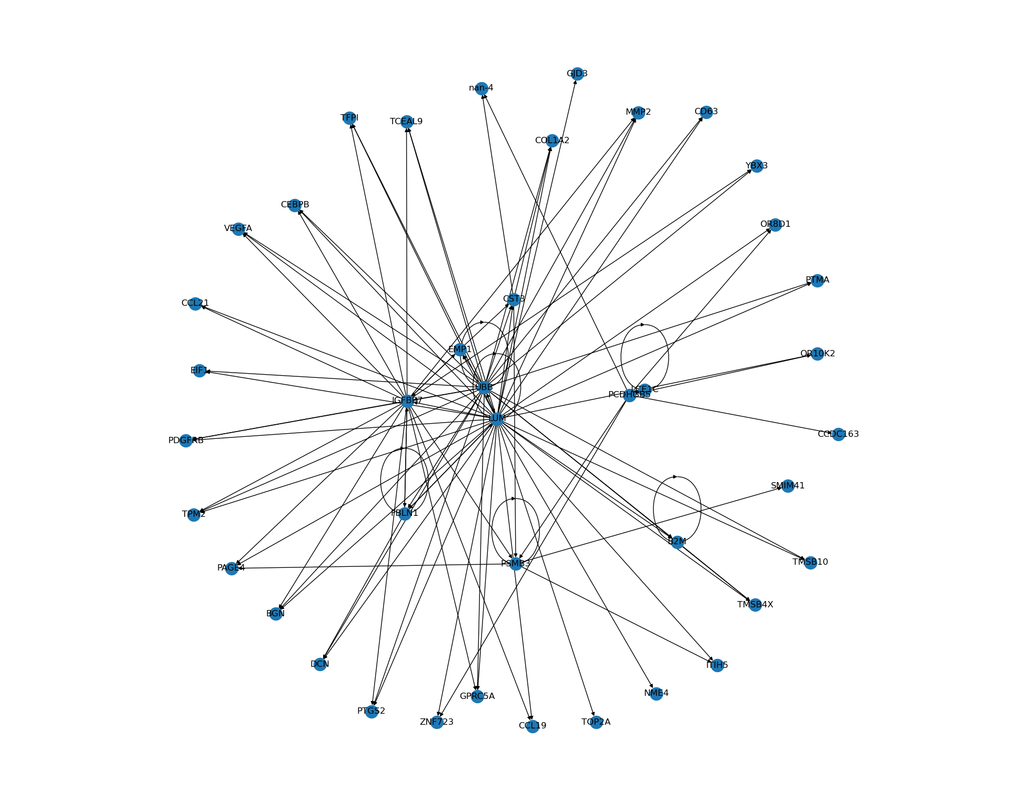
- gene network inference: generate a gene network from any cell or cell cluster in your scRNAseq dataset