Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
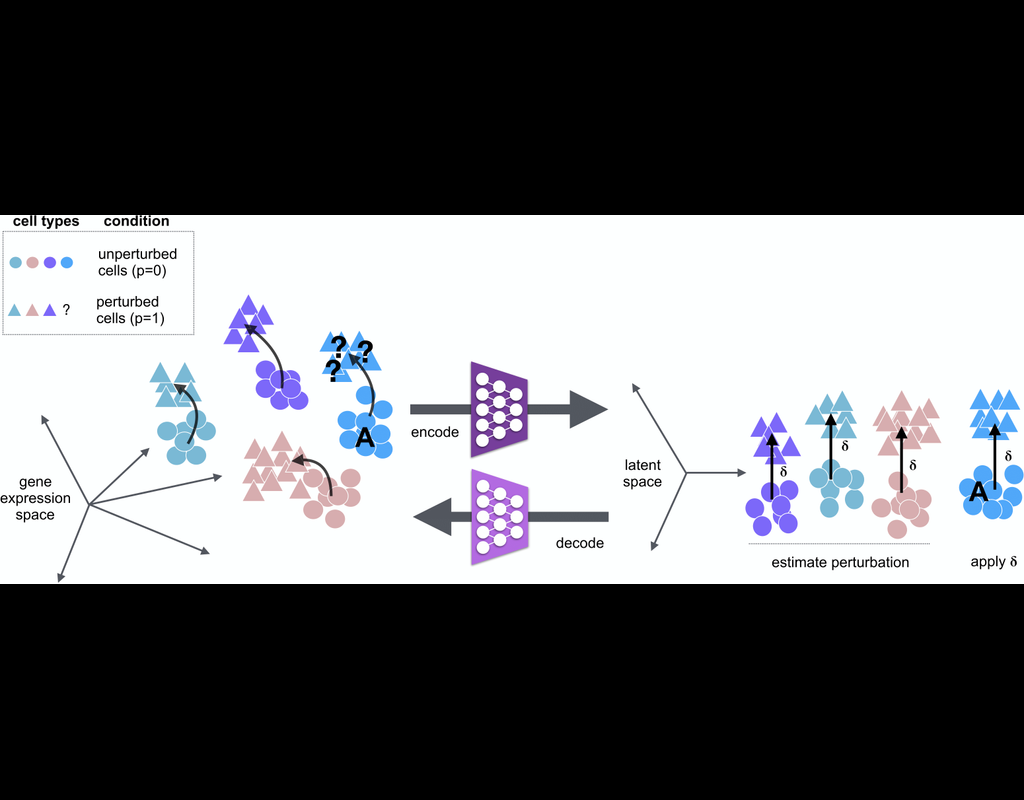
scGen is a generative model to predict single-cell perturbation response across cell types, studies and species (Nature Methods, 2019). scGen is implemented using the scvi-tools framework.
What you can do with scGen:
Train on a dataset with multiple cell types and conditions and predict the perturbation effect on the cell type which you only have in one condition. This scenario can be extended to multiple species where you want to predict the effect of a specific species using another or all the species.
Train on a dataset where you have two conditions (e.g. control and perturbed) and predict on second dataset with similar genes.
Remove batch effect on labeled data. In this scenario you need to provide cell_type and batch labels to the method. Note that batch_removal does not require all cell types to be present in all datasets (batches). If you have dataset specific cell type it will preserved as before.
We assume there exist two conditions in you dataset (e.g. control and perturbed). You can train the model and with your data and predict the perturbation for the cell type/species of interest.
We recommend to use normalized data for the training. A simple example for normalization can be performed using scanpy