Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
Single-cell sequencing is an increasingly used technology and has promising applications in basic research and clinical translations. However, genotyping methods developed for bulk sequencing data have not been well adapted for single-cell data. In this notebook, we introduce cellSNP-lite for genotyping in single-cell sequencing data for both droplet and well-based platforms.
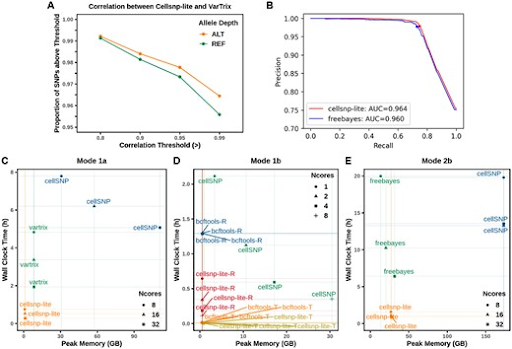
Cellsnp-lite is a C/C++ tool for efficient genotyping bi-allelic SNPs on single cells. You can use cellsnp-lite after read alignment to obtain the snp x cell pileup UMI or read count matrices for each alleles of given or detected SNPs.
cellSNP-lite aims to pileup the expressed alleles in single-cell or bulk RNA-seq data, which can be directly used for donor deconvolution in multiplexed single-cell RNA-seq data, particularly with vireo, which assigns cells to donors and detects doublets, even without genotyping reference.
Cellsnp-lite has following features:
- Wide applicability: cellsnp-lite can take data from various omics as input, including RNA-seq, DNA-seq, ATAC-seq, either in bulk or single cells.
- Simplified user interface that supports parallel computing, cell barcode and UMI tags.
- High efficiency in terms of running speed and memory usage with highly concordant results compared to existing methods.