Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
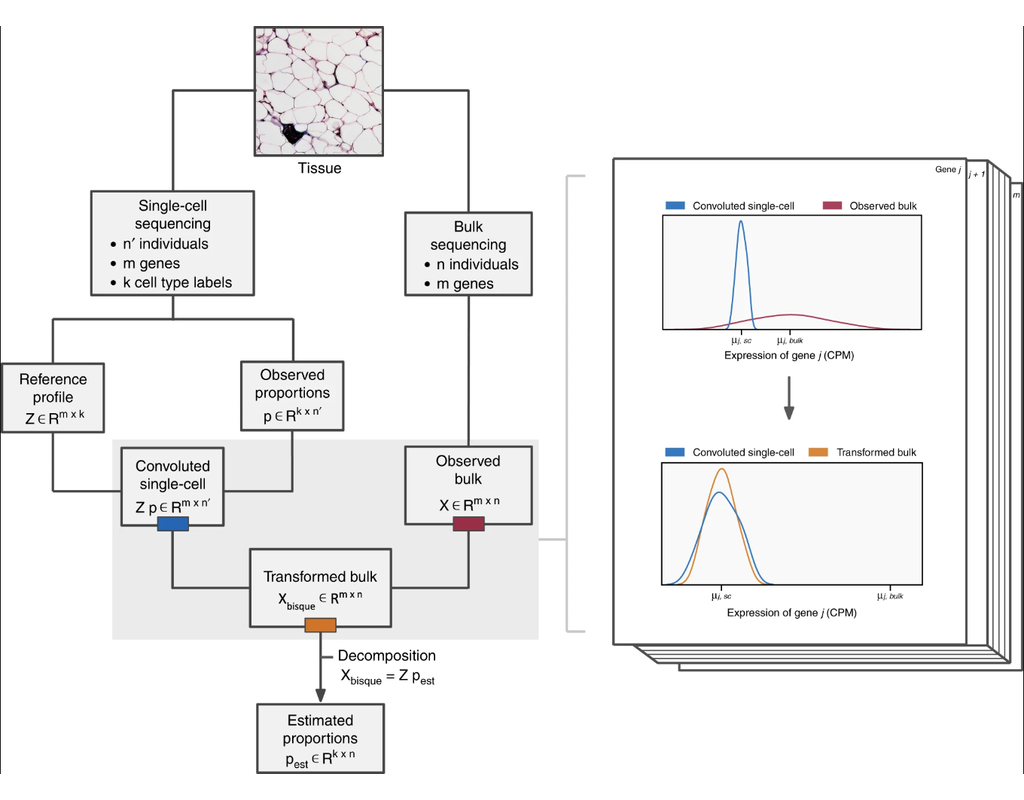
An R toolkit for accurate and efficient estimation of cell composition ('decomposition') from bulk expression data with single-cell information.
Bisque provides two modes of operation:
* Reference-based decomposition: This method utilizes single-cell data to decompose bulk expression. Bisque assumes that both single-cell and bulk counts are measured from the same tissue. Specifically, the cell composition of the labeled single-cell data should match the expected physiological composition. While Bisque doesn't explicitly require matched samples, Bisque expect having samples with both single-cell and bulk expression measured will provide more accurate results.
* Marker-based decomposition: This method utilizes marker genes alone to decompose bulk expression when a reference profile is not available. Single-cell data is not explicitly required but can be used to identify these marker genes. This method captures relative abundances of a cell type across individuals. Note that these abundances are not proportions, so they cannot be compared between different cell types.