Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
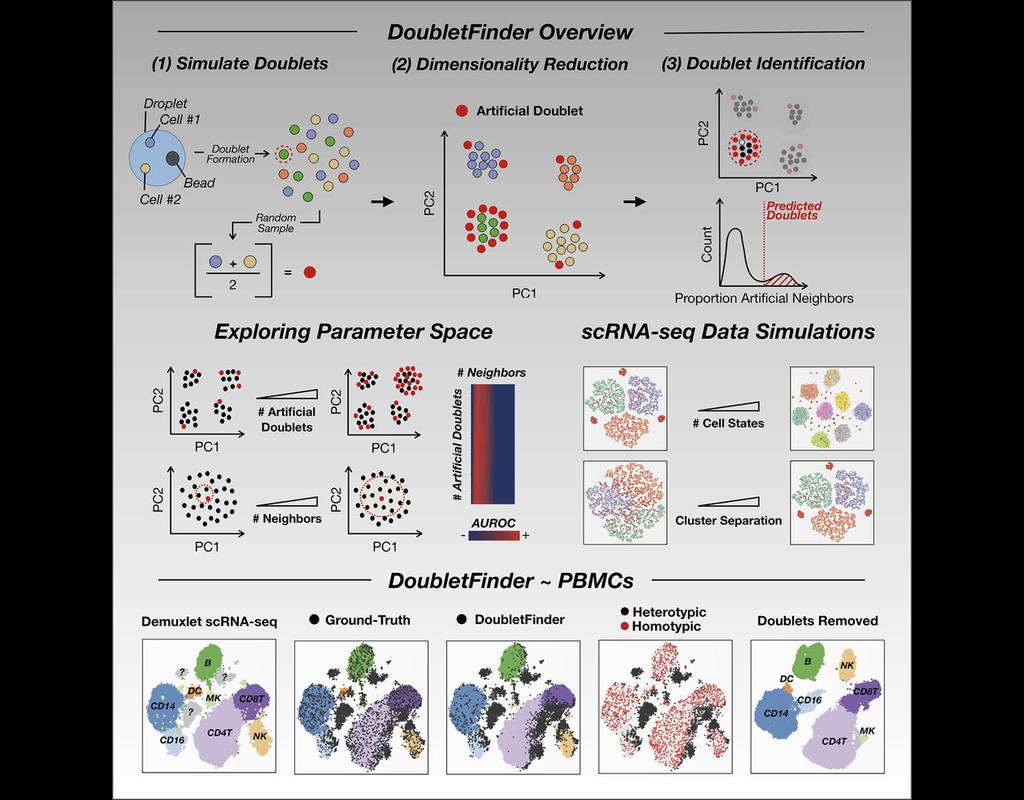
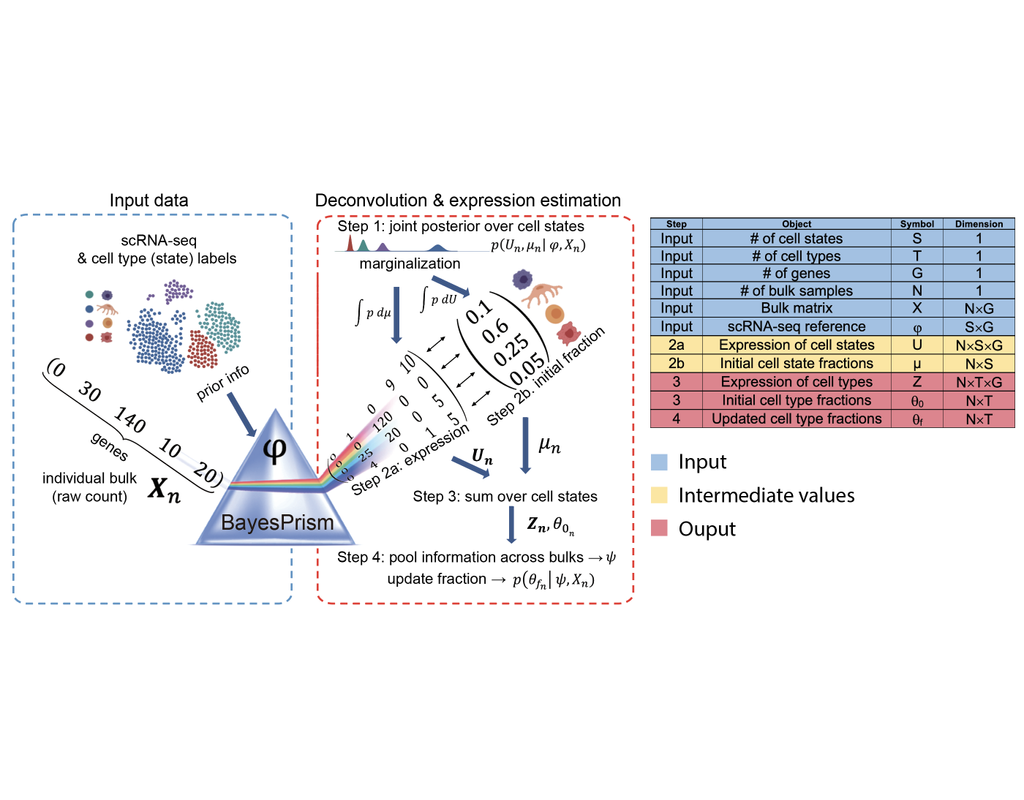
Reconstructing cell type compositions and their gene expression from bulk RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) datasets is an ongoing challenge in cancer research. BayesPrism (Chu, T., Wang, Z., Pe’er, D. et al., 2022) is a Bayesian method used to predict cellular composition and gene expression in individual cell types from bulk RNA-seq datasets, with scRNA-seq as references.
This notebook illustrates an example workflow for bulk RNA-seq deconvolution using BayesPrism. The notebook content is inspired by BayesPrism's vignette and modified to demonstrate how the tool works on BioTuring's platform.