Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
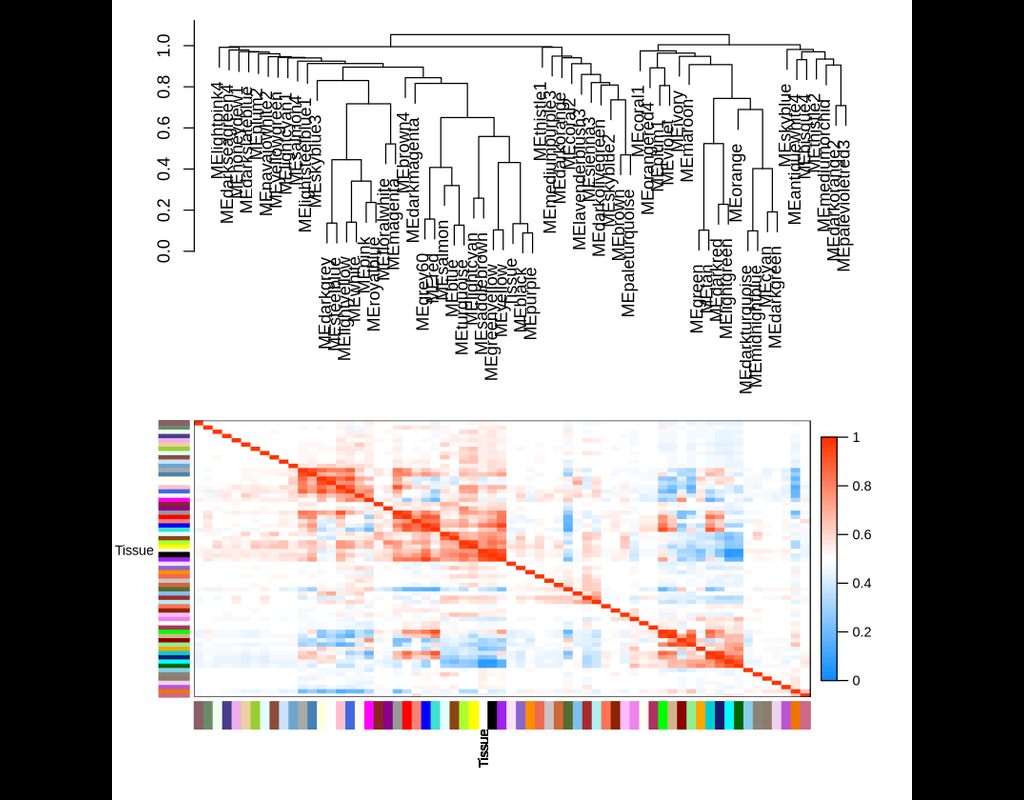
WGCNA: an R package for Weighted Gene Correlation Network Analysis
Correlation networks are increasingly being used in bioinformatics applications. For example, weighted gene co-expression network analysis is a systems biology method for describing the correlation patterns among genes across microarray samples. Weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) can be used for:
- Finding clusters (modules) of highly correlated genes
- Summarizing such clusters using the module eigengene or an intramodular hub gene
- Relating modules to one another and to external sample traits (using eigengene network methodology)
- For calculating module membership measures
All of these are important for identifying potential candidate genes associated with measured traits as well as identifying genes that are consistently co-expressed and could be contributing to similar molecular pathways. Using WGCNA is also extremely useful statistically as it accounts for inter-individual variation in gene expression and alleviates issues associated with multiple testing.