Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
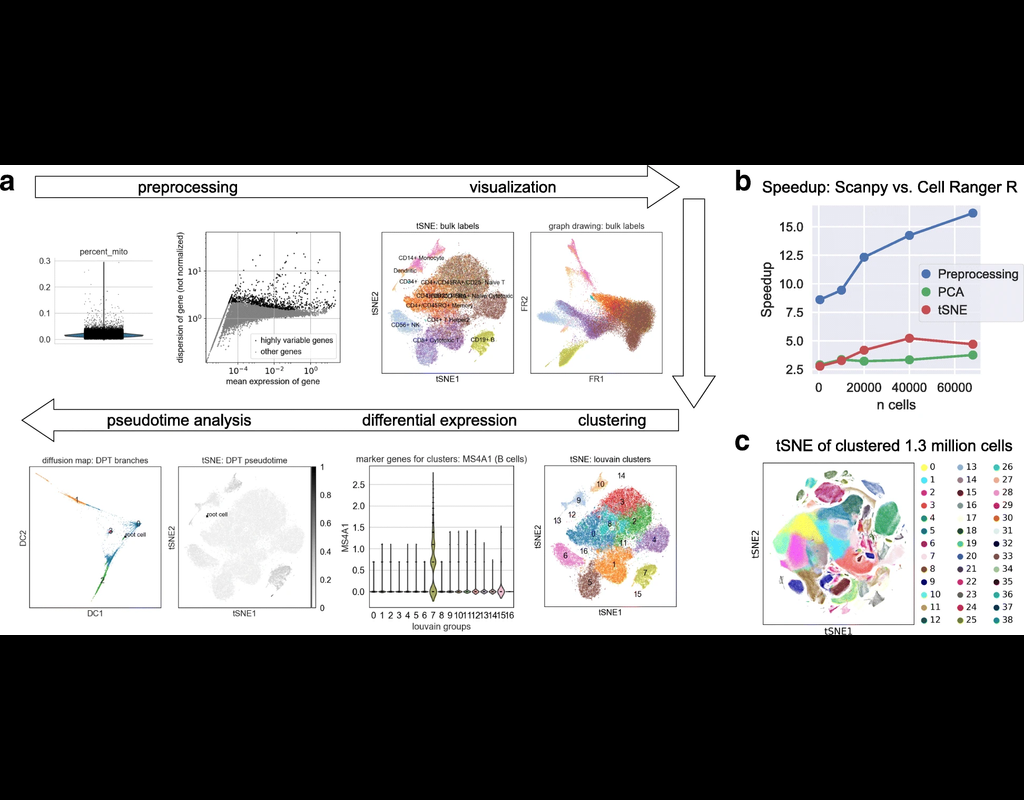
SCANPY integrates the analysis possibilities of established R-based frameworks and provides them in a scalable and modular form.
Specifically, SCANPY provides preprocessing comparable to SEURAT and CELL RANGER, visualization through TSNE, graph-drawing and diffusion maps, clustering similar to PHENOGRAPH, identification of marker genes for clusters via differential expression tests and pseudotemporal ordering via diffusion pseudotime, which compares favorably with MONOCLE 2, and WISHBONE.