Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
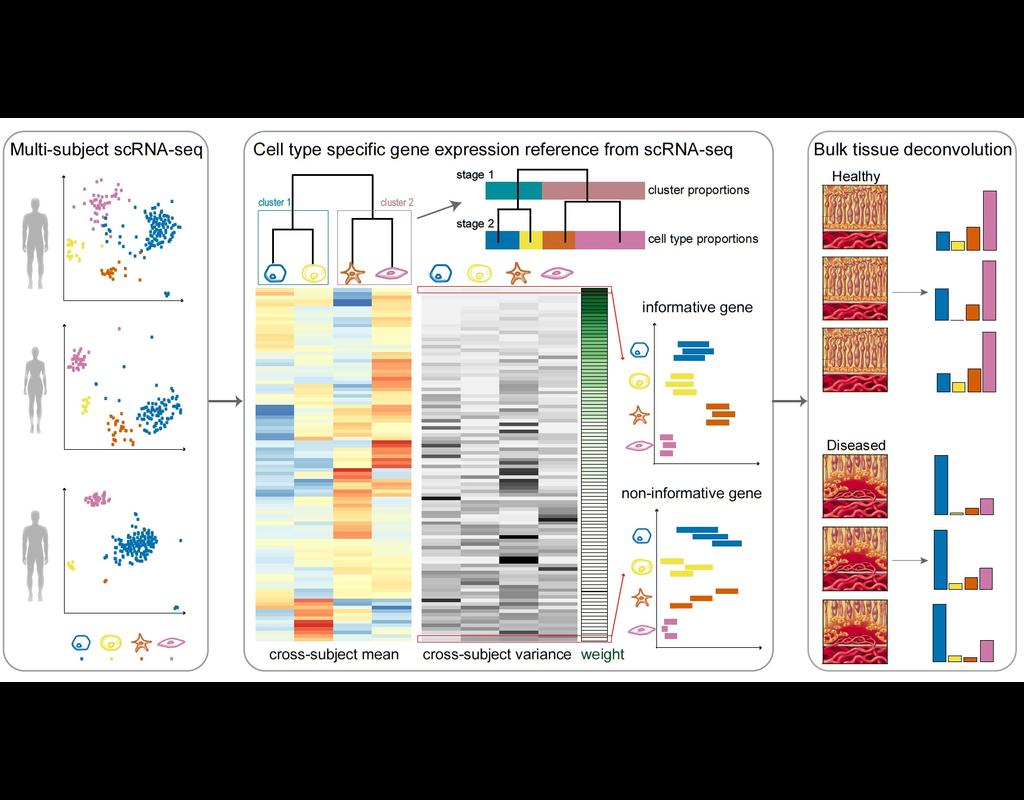
Knowledge of cell type composition in disease relevant tissues is an important step towards the identification of cellular targets of disease. MuSiC is a method that utilizes cell-type specific gene expression from single-cell RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data to characterize cell type compositions from bulk RNA-seq data in complex tissues.
By appropriate weighting of genes showing cross-subject and cross-cell consistency, MuSiC enables the transfer of cell type-specific gene expression information from one dataset to another.
MuSiC enables the characterization of cellular heterogeneity of complex tissues for understanding of disease mechanisms. As bulk tissue data are more easily accessible than single-cell RNA-seq, MuSiC allows the utilization of the vast amounts of disease relevant bulk tissue RNA-seq data for elucidating cell type contributions in disease.
This notebook provides a walk through tutorial on how to use MuSiC to estimate cell type proportions from bulk sequencing data based on multi-subject single cell data by reproducing the analysis in MuSiC paper, now is published on Nature Communications.