Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
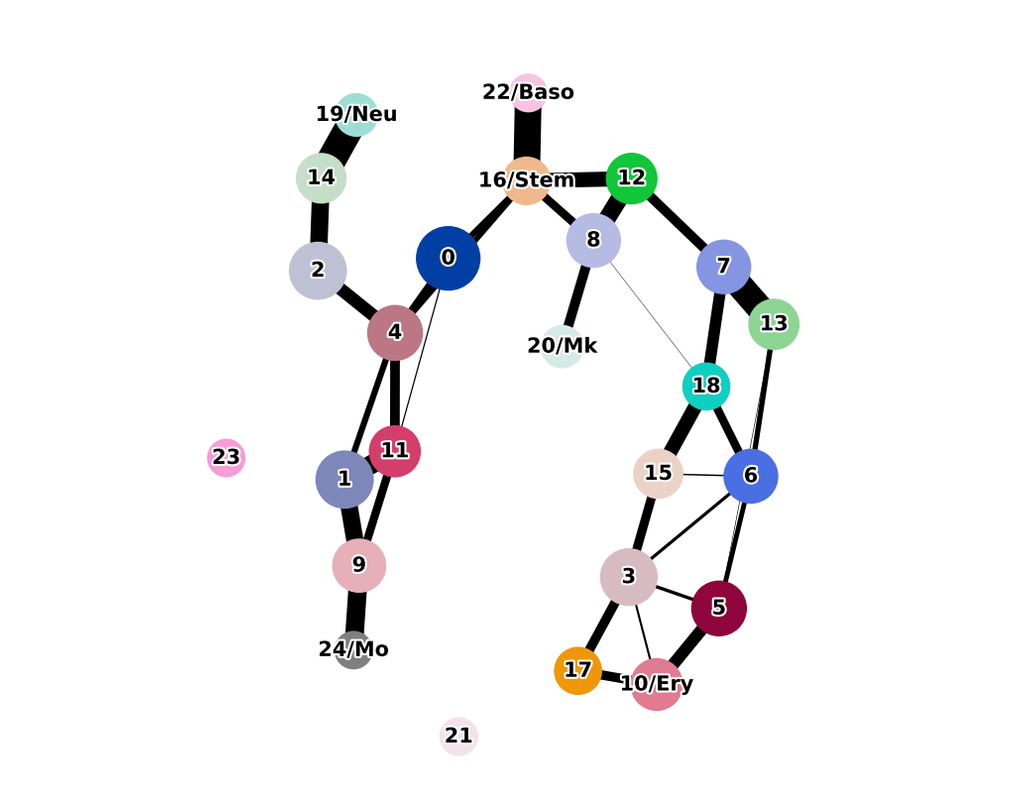
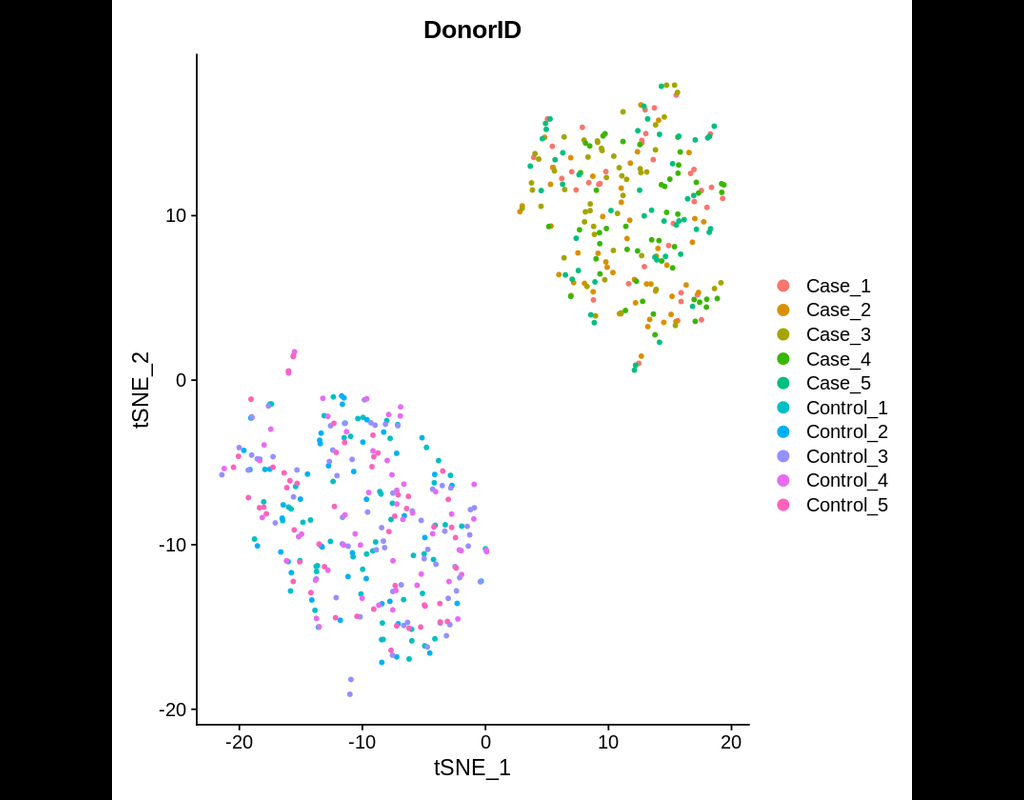
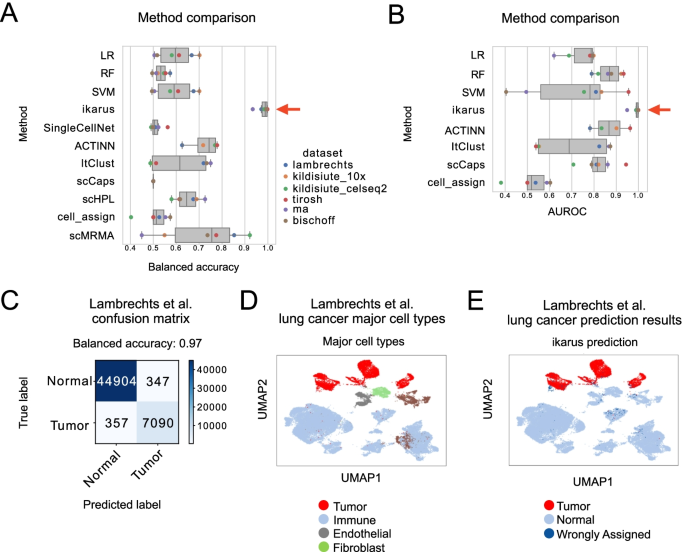
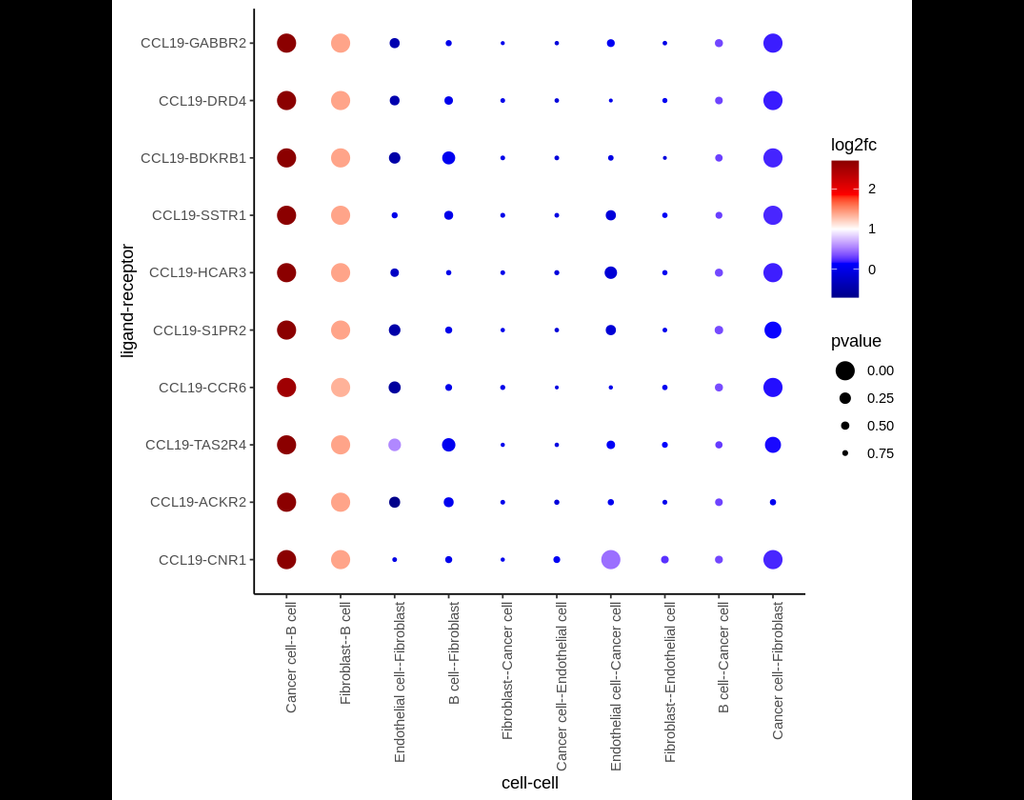
Dampened weighted least squares (DWLS) is an estimation method for gene expression deconvolution, in which the cell-type composition of a bulk RNA-seq data set is computationally inferred. This method corrects common biases towards cell types that are characterized by highly expressed genes and/or are highly prevalent, to provide accurate detection across diverse cell types.
To begin, the user must input a bulk RNA-seq data set, along with a labeled representative single-cell RNA-seq data set that will serve to generate cell-type-specific gene expression profiles. Ideally, the single-cell data set will contain cells from all cell types that may be found in the bulk data. DWLS will return the cell-type composition of the bulk data.