Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
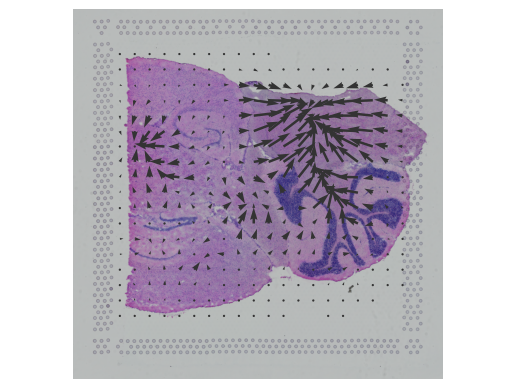
In this notebook, we present COMMOT (COMMunication analysis by Optimal Transport) to infer cell-cell communication (CCC) in spatial transcriptomic, a package that infers CCC by simultaneously considering numerous ligand–receptor pairs for either spatial transcriptomic data or spatially annotated scRNA-seq data equipped with spatial distances between cells estimated from paired spatial imaging data.
A collective optimal transport method is developed to handle complex molecular interactions and spatial constraints. Furthermore, we introduce downstream analysis tools to infer spatial signaling directionality and genes regulated by signaling using machine learning models.