Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
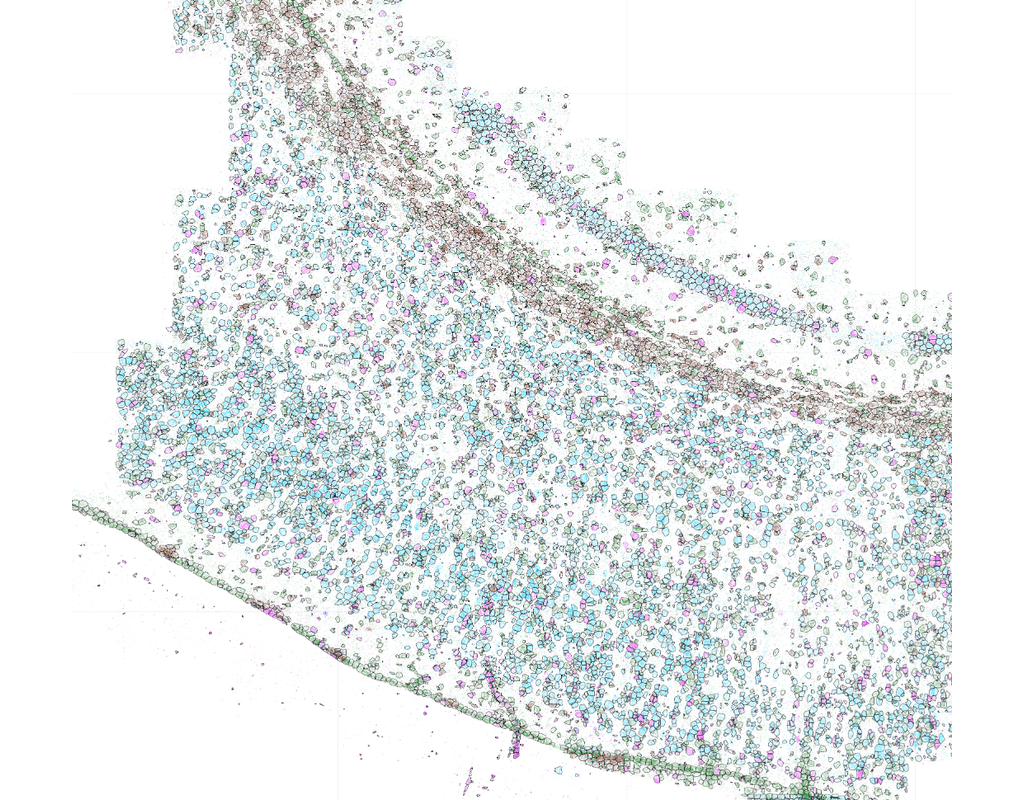
Single-molecule spatial transcriptomics protocols based on in situ sequencing or multiplexed RNA fluorescent hybridization can reveal detailed tissue organization. However, distinguishing the boundaries of individual cells in such data is challenging and can hamper downstream analysis.
Baysor is a tool for performing cell segmentation on imaging-based spatial transcriptomics data. It optimizes two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) cell boundaries segmentation considering the likelihood of transcriptional composition, size and shape of the cell (cell morphology). The approach can take into account nuclear or cytoplasm staining, however, can also perform segmentation based on the detected molecules alone.